Dividend stocks that do not pay dividends are great for investors as they mean no taxable income until there is a gain. You can also control the time you pay taxes on equity holdings by not paying dividends. Warren Buffett, a wise investor, only invests in value stocks. He can afford to buy no dividend stocks at a margin of safety. This is why he took bold steps during the financial crisis by making banking stock play. You don't need to understand the tax implications of dividends to benefit from no dividend stocks.
High-dividend stocks outperform no dividend stocks
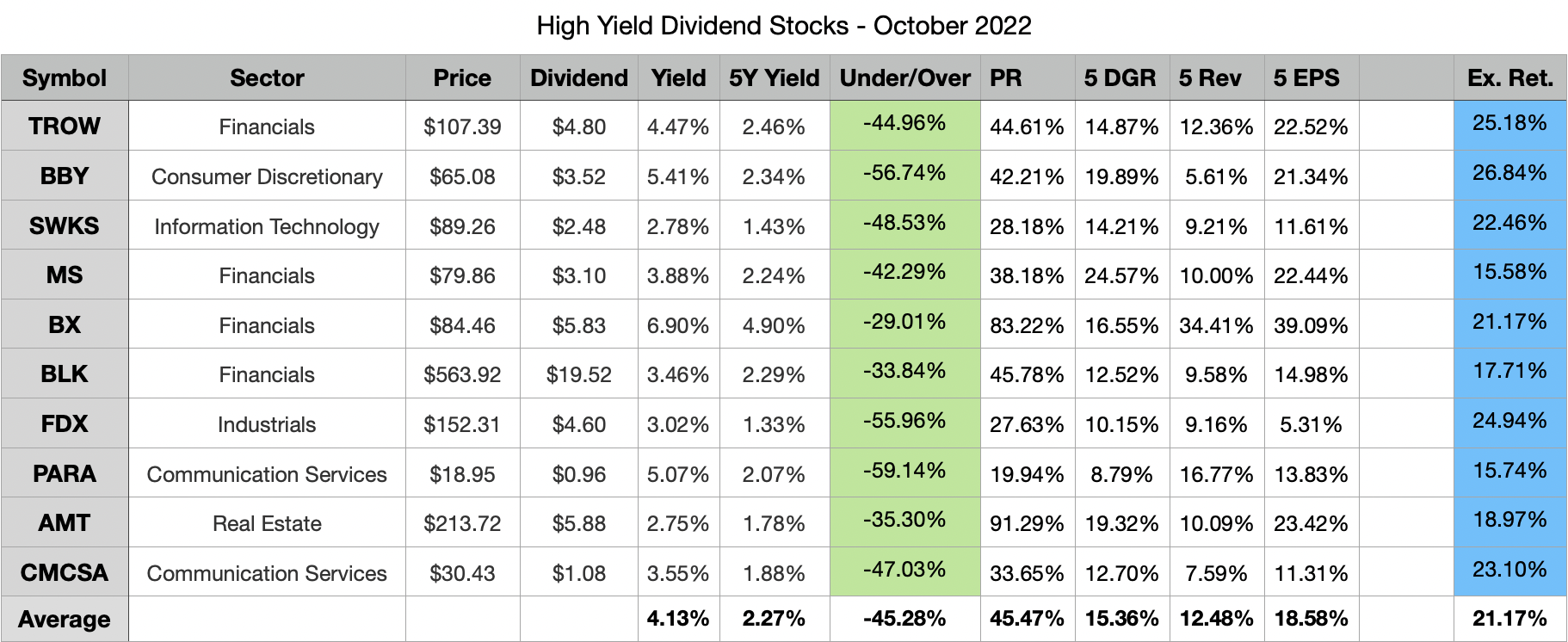
If you are looking for a stock that is outperforming the broader market, consider dividend stocks. BlackRock and Comcast are among the dividend-paying companies that have outperformed other stocks in recent months. Morningstar's US High Dividend Yield Index is leading the market with 14.4% points. This is a significant margin. Last year, it beat the U.S. markets by 9.8%.
Since 1973, dividend-paying stock have outperformed those that don't pay dividends. They have accrued more money and generated higher total returns than those with no dividends. The highest returns have been achieved by dividend initiators, although they also experience lower volatility. In addition, dividend-paying shares are more likely be to earn positive monthly returns. Hence, if you are looking for a long-term investment strategy, consider buying dividend-paying stocks.

Companies at growth stage seldom pay dividends
There are many reasons companies that are in growth stages rarely pay dividends. In some cases, companies simply do not make enough money to pay dividends. On the other hand, some companies never stop reinvesting their profits. These companies are growth stocks and their reinvestments can have an impact on the company's stock price and growth. Investors find this a great trade-off. A good example is Amazon, which rarely pays dividends, despite its high growth potential.
Amazon and Apple are two of the most successful examples of such companies. They have both achieved great success and have a worldwide footprint. These companies expand their operations and use profits to increase their sales in both cases. They never paid dividends in cash and instead used profits to expand the business. Microsoft didn't pay any dividends until it was valued at $350Billion. As a consequence, long-term shareholders and the founders became multi-millionaires. However, established, larger companies pay more dividends and are more concerned about increasing shareholder wealth.
Dividends have tax implications
Many income investors don't realize the tax implications of holding no dividend stocks despite the obvious tax benefits. The tax code is now more than 10 million words, compared to only 1.4 million in 1955. Further, the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act makes it even more difficult to navigate. You need to be careful when investing in income-producing properties. Make sure to invest in tax-advantaged accounts if you want maximum tax benefit.
Nondividend distributions are not taxable because they do not represent earnings of the corporation. They are instead a return of capital. These investments are taxable only when the cost basis must be deducted from your taxes. Nondividend distributions, particularly when reinvested, may be exempt from tax. Investors must be aware of the tax implications of dividend stocks if they want to maximize their profit.
Sharpe ratio for portfolios that contain zero dividends
For evaluating investment opportunities, the Sharpe ratio of zero dividend equity portfolios is a popular indicator. It is calculated by subtracting the portfolio's rate return from its risk-free, which is typically the yield on U.S. Treasury bond bonds. The portfolio's standard deviation divides the excess investment return. In other words, this formula assumes that the returns are normally distributed.
The Sharpe rate is calculated using the risk free rate or the T-Bill for 90 days. This metric tells investors how much extra return they can expect. Investors have to accept higher returns in exchange for taking on additional risk. The Sharpe Ratio is calculated by adding the risk-free rate to the investment and subtracting its standard deviation.
FAQ
How do I choose a good investment company?
It is important to find one that charges low fees, provides high-quality administration, and offers a diverse portfolio. The type of security that is held in your account usually determines the fee. While some companies do not charge any fees for cash holding, others charge a flat fee per annum regardless of how much you deposit. Others charge a percentage of your total assets.
Also, find out about their past performance records. Companies with poor performance records might not be right for you. Companies with low net asset values (NAVs) or extremely volatile NAVs should be avoided.
You should also check their investment philosophy. To achieve higher returns, an investment firm should be willing and able to take risks. If they aren't willing to take risk, they may not meet your expectations.
Is stock a security that can be traded?
Stock is an investment vehicle where you can buy shares of companies to make money. This is done through a brokerage that sells stocks and bonds.
You can also directly invest in individual stocks, or mutual funds. There are more mutual fund options than you might think.
The difference between these two options is how you make your money. Direct investment is where you receive income from dividends, while stock trading allows you to trade stocks and bonds for profit.
Both cases mean that you are buying ownership of a company or business. However, if you own a percentage of a company you are a shareholder. The company's earnings determine how much you get dividends.
Stock trading gives you the option to either short-sell (borrow a stock) and hope it drops below your cost or go long-term by holding onto the shares, hoping that their value increases.
There are three types of stock trades: call, put, and exchange-traded funds. Call and Put options give you the ability to buy or trade a particular stock at a given price and within a defined time. ETFs, also known as mutual funds or exchange-traded funds, track a range of stocks instead of individual securities.
Stock trading is very popular since it allows investors participate in the growth and management of companies without having to manage their day-today operations.
Stock trading is not easy. It requires careful planning and research. But it can yield great returns. You will need to know the basics of accounting, finance, and economics if you want to follow this career path.
What is the role of the Securities and Exchange Commission?
SEC regulates brokerage-dealers, securities exchanges, investment firms, and any other entities involved with the distribution of securities. It enforces federal securities regulations.
Statistics
- "If all of your money's in one stock, you could potentially lose 50% of it overnight," Moore says. (nerdwallet.com)
- For instance, an individual or entity that owns 100,000 shares of a company with one million outstanding shares would have a 10% ownership stake. (investopedia.com)
- US resident who opens a new IBKR Pro individual or joint account receives a 0.25% rate reduction on margin loans. (nerdwallet.com)
- Our focus on Main Street investors reflects the fact that American households own $38 trillion worth of equities, more than 59 percent of the U.S. equity market either directly or indirectly through mutual funds, retirement accounts, and other investments. (sec.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Trade Stock Markets
Stock trading can be described as the buying and selling of stocks, bonds or commodities, currency, derivatives, or other assets. Trading is French for "trading", which means someone who buys or sells. Traders are people who buy and sell securities to make money. This is the oldest type of financial investment.
There are many ways you can invest in the stock exchange. There are three basic types: active, passive and hybrid. Passive investors do nothing except watch their investments grow while actively traded investors try to pick winning companies and profit from them. Hybrid investors take a mix of both these approaches.
Index funds that track broad indexes such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average or S&P 500 are passive investments. This method is popular as it offers diversification and minimizes risk. You just sit back and let your investments work for you.
Active investing means picking specific companies and analysing their performance. Active investors look at earnings growth, return-on-equity, debt ratios P/E ratios cash flow, book price, dividend payout, management team, history of share prices, etc. They will then decide whether or no to buy shares in the company. They will purchase shares if they believe the company is undervalued and wait for the price to rise. If they feel the company is undervalued, they'll wait for the price to drop before buying stock.
Hybrid investments combine elements of both passive as active investing. For example, you might want to choose a fund that tracks many stocks, but you also want to choose several companies yourself. In this scenario, part of your portfolio would be put into a passively-managed fund, while the other part would go into a collection actively managed funds.